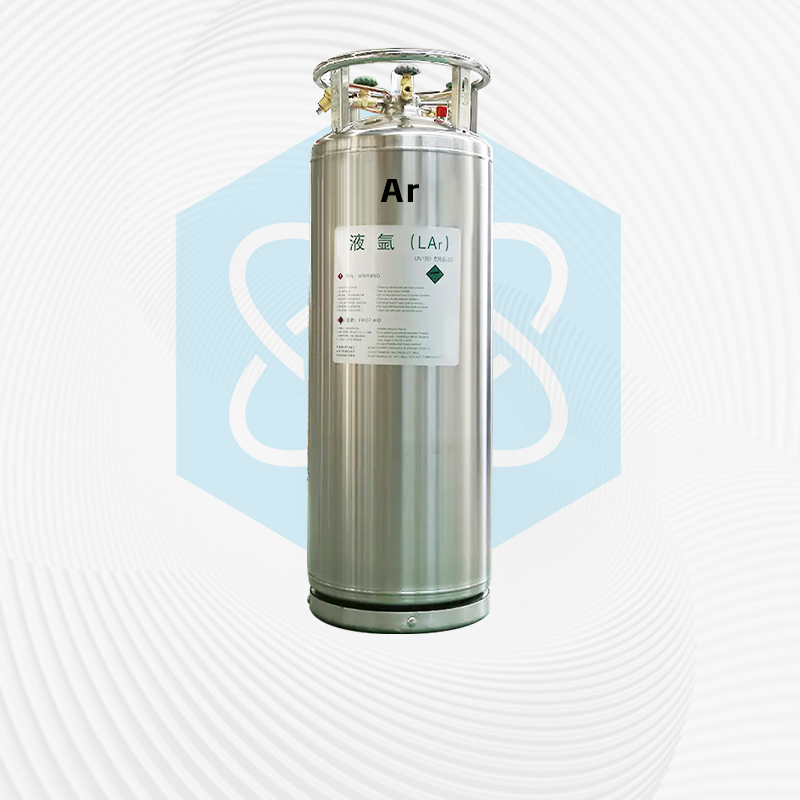
Liquid argon, also known as argon in English, is an inert gas. It is non-toxic in itself, and there is a risk of suffocation when the concentration in the air is high. The symptoms of suffocation are: initially, there is an increase in breathing, decreased attention, muscle movement disorders, followed by a decrease in judgment, loss of all senses, unstable emotions, and overall fatigue, leading to nausea, vomiting, weakness, spasms, drowsiness, and ultimately death. Harmless to the environment, waste can be directly discharged into the atmosphere.

First aid measures
Skin contact: Contact with liquid argon can cause frostbite. Rinse the affected area with water and seek medical attention
Eye contact: Open the eyelids and rinse with physiological saline or flowing water, seek medical attention.
Inhalation: Move the patient to a place with fresh air, keep the respiratory tract unobstructed, administer oxygen when breathing is difficult, perform respiratory resuscitation when breathing stops, and perform cardiopulmonary resuscitation when heartbeat stops; Seek medical attention.
Firefighting measures
Hazard characteristics: Argon itself does not burn, but containers and equipment containing argon gas can experience a sharp increase in pressure inside the container when exposed to open flames and high temperatures, leading to an explosion. Water should be used to cool the container in the fire.
Fire extinguishing method: Cool the container in the fire with water. Use fire extinguishing agents that are suitable for the fire environment. If possible, move the container from the fire to an open area.
Leakage emergency response
Quickly evacuate personnel from the contaminated area to the upwind, isolate them, and strictly restrict entry and exit. It is recommended that emergency response personnel wear self-contained positive pressure respirators and general work clothes. Cut off the source of leakage as much as possible. Reasonable ventilation and accelerated diffusion. Leakage containers should be properly handled, repaired, and inspected before use.
Protective measures
Engineering control: closed production process and enhanced ventilation
Respiratory system protection: When the concentration in the air exceeds the standard, the scene should be evacuated quickly, and air respirators or oxygen respirators should be worn for rescue and accident handling.
Eye protection: Face masks should be worn when in contact with liquid argon environments.
Body protection: Cold clothing should be worn in low-temperature work areas.
Hand protection: Wear cold gloves in low temperature environments
Other protective measures: Smoking is prohibited at the workplace, and drinking alcoholic beverages should be avoided before work. Conduct pre employment and regular medical examinations. Entry into restricted spaces or high concentration areas for work must be supervised by someone.
Handling and storage
Precautions for operation and disposal: Closed operation, strengthened ventilation, equipped with accident forced ventilation equipment, and operators must undergo specialized training. Work with a certificate and strictly follow the operating procedures during operation. Control the filling speed during filling. The filling time shall not be less than 30 minutes. Strictly prevent frostbite from liquid argon leakage.
Storage precautions: Store in a ventilated warehouse, away from sparks, heat sources, and gas cylinders should have anti falling measures. The storage temperature should not exceed 30 ℃. The storage area should be equipped with emergency response equipment for leaks.